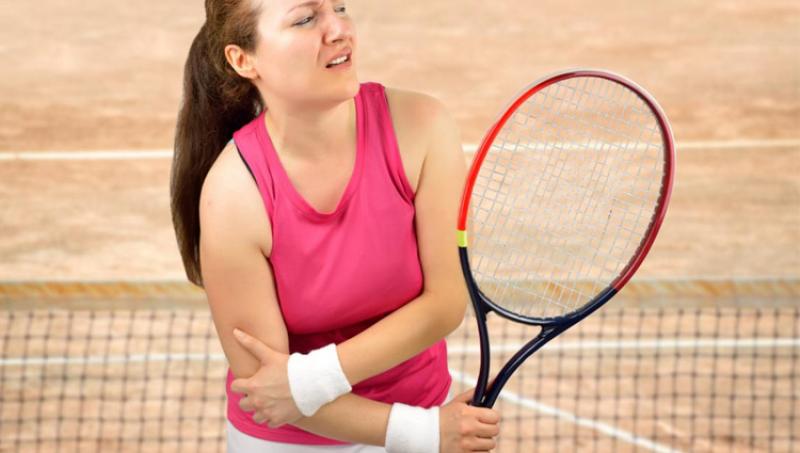
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can cause this condition. However, several other sports and activities can also put you at risk. The tennis elbow is an inflammation of the tendons that join the forearm muscles on the outside of the elbow. The forearm muscles and tendons become damaged from overuse — repeating the same motions again and again. This leads to pain and tenderness on the outside of the elbow.
Anatomy
Your elbow joint is a joint made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus) and the two bones in your forearm (radius and ulna). There are bony bumps at the bottom of the humerus called epicondyles. The bony bump on the outside (lateral side) of the elbow is called the lateral epicondyle. Muscles, ligaments, and tendons hold the elbow joint together.
Lateral epicondylitis, or tennis elbow, involves the muscles and tendons of your forearm. Your forearm muscles extend your wrist and fingers. Your forearm tendons — often called extensors — attach the muscles to bone. They attach to the lateral epicondyle. The tendon usually involved in the tennis elbow is called the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis (ECRB).
Kottakkal Ayurveda is a center for Ayurvedic massage, treatment, healing, herbal medicine, and lifestyle practices. Our team of dedicated Ayurveda practitioners, trained in the art of Ayurveda are here to support your transformation and wellbeing. Kottakkal Ayurvedic Treatment Centre is the premier provider of Ayurvedic services in Dubai (Deira, Satwa), Ajman and we’re excited to share these restorative techniques with you.
Cause
Overuse:
Recent studies show that the tennis elbow is often due to damage to a specific forearm muscle. The extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) muscle helps stabilize the wrist when the elbow is straight. This occurs during a tennis groundstroke, for example. When the ECRB is weakened from overuse, microscopic tears form in the tendon where it attaches to the lateral epicondyle. This leads to inflammation and pain. The ECRB may also be at increased risk for damage because of its position. As the elbow bends and straightens, the muscle rubs against bony bumps. This can cause gradual wear and tear of the muscle over time.
Athletes are not the only people who get tennis elbow. Many people with tennis elbow participate in work or recreational activities that require repetitive and vigorous use of the forearm muscle. Painters, plumbers, and carpenters are particularly prone to developing tennis elbow. Studies have shown that auto workers, cooks, and even butchers get tennis elbow more often than the rest of the population. It is thought that the repetition and weight lifting required in these occupations leads to injury.
Age
Most people who get tennis elbow are between the ages of 30 and 50, although anyone can get tennis elbow if they have the risk factors. In racquet sports like tennis, improper stroke technique and improper equipment may be risk factors.
Unknown
Lateral epicondylitis can occur without any recognized repetitive injury. This occurrence is called “insidious” or of an unknown cause.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tennis elbow develop gradually. In most cases, the pain begins as mild and slowly worsens over weeks and months. There is usually no specific injury associated with the start of symptoms.
Common signs and symptoms of tennis elbow include:
Pain or burning on the outer part of your elbow
Weak grip strength
Swollen, red, and warm elbow
Tenderness and inflammation in the outer part of the elbow
Pain on movement especially while lifting objects
Dull ache even in resting position
Pain radiating downward into the forearms
Elbow stiffness in the morning
Weakness in the wrist or elbow joint
The symptoms are often worsened with forearm activity, such as holding a racquet, turning a wrench, or shaking hands. Your dominant arm is most often affected; however, both arms can be affected.
Ayurvedic Treatment
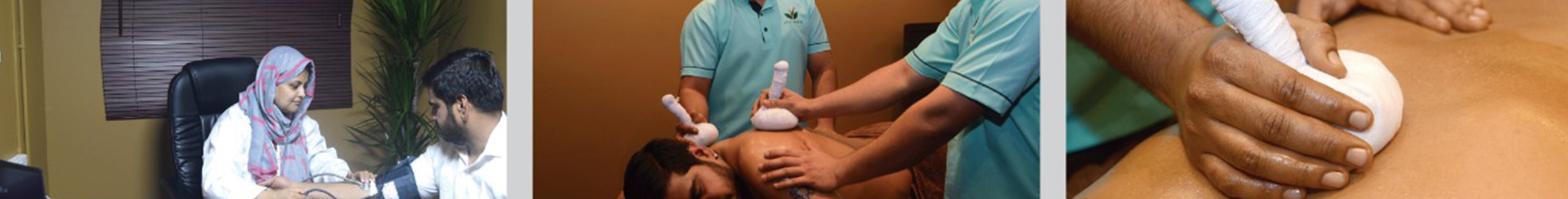
Ayurvedic approach to the treatment of Tennis Elbow condition includes administration of anti-inflammatory Ayurvedic natural herbal medicines, application of medicated oils/powders to the area with mild Abhyanga with specific oils, churnapindaswedam or patrapotalaswedam, Dhanyamladhara or sweating treatment (Swedana), Lepanam, herbal bandages, and Pichu treatment is also recommended depending upon the severity of the condition. The treatments are aimed at improving the blood circulation and reducing the inflammation and strain to the affected tendon rather than painkilling.
 Ajman:052 6474941
Ajman:052 6474941  Dubai 055 3699446
Dubai 055 3699446 Satwa +971 55 610 3056
Satwa +971 55 610 3056 Sharjah +971 50 6545235
Sharjah +971 50 6545235